总结
- CI 设计
- 什么分支(监听范围)
- 什么事件(时间钩子)
- 什么命令(操作)
- CI 流程
- Install:依赖安装
- Lint:统一代码风格
- Test:单元测试
- Preview:生成供测试人员进行检查的网址。
- Audit: 使用 npm audit 或者 snyk 检查依赖的安全风险。可详查文章如何检测有风险依赖
- Quality: 使用 SonarQube 检查代码质量。
- Container Image: 使用 trivy 扫描容器镜像安全风险。
- End to End: 使用 Playwright 进行 UI 自动化测试。
- Bundle Chunk Size Limit: 使用 size-limit 限制打包体积,打包体积过大则无法通过合并。
- Performance (Lighthouse CI): 使用 lighthouse CI 为每次 PR 通过 Lighthouse 打分,如打分过低则无法通过合并。
- Matrix:要测试不同
node.js环境下的表现,可使用 matrix
疑问
提问
[ ] 你们在 CI 中做了那些检测
使用 audit 校验检查依赖的安全风险
触发 eslint 校验
运行单元测试
[x] 使用 github actions 配置 lint
# 校验
lint:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest # 指定环境
steps: #执行步骤
- uses: actions/checkout@v2.4.2
- name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v3.4.1
with:
node-version: 16.x
- name: Install Dependencies
# if: steps.cache-node-modules.outputs.cache-hit != 'true'
run: yarn
# 校验
- name: Eslint
run: yarn lint
- [x] 使用 github actions 配置 audit
# 检查依赖的安全风险
audit:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps: #执行步骤
- uses: actions/checkout@v2.4.2
- name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v3.4.1
with:
node-version: 16.x
# 执行检查-只针对打包
- name: Run a Security Audit
continue-on-error: true # 因为现在还没精力去调配依赖,报错先跳过
run: npm audit --only=prod
1. 前提提要、场景
介绍完 CI/CD 后,本章开始通过 Github Actions 实现 CI。
实现以下流程:
- Install:依赖安装
- Lint:统一代码风格
- Test:单元测试
- Preview:生成供测试人员进行检查的网址。(比较复杂,后续实现)
1.1 更高级的 CI
Lint 和 Test 仅是 CI 中最常见的阶段。为了保障我们的前端代码质量,还可以添加以下阶段。
- Audit: 使用 npm audit 或者 snyk 检查依赖的安全风险。可详查文章如何检测有风险依赖
- Quality: 使用 SonarQube 检查代码质量。
- Container Image: 使用 trivy 扫描容器镜像安全风险。
- End to End: 使用 Playwright 进行 UI 自动化测试。
- Bundle Chunk Size Limit: 使用 size-limit 限制打包体积,打包体积过大则无法通过合并。
- Performance (Lighthouse CI): 使用 lighthouse CI 为每次 PR 通过 Lighthouse 打分,如打分过低则无法通过合并。
- Matrix:要测试不同
node.js环境下的表现,可使用 matrixyamljobs: example_matrix: strategy: matrix: version: [10, 12, 14] steps: - uses: actions/setup-node@v3 with: node-version: ${{ matrix.version }}
2. Git Workflow 场景
假设一个极其简单的 Git Workflow 场景
- 每个人在功能分支进行新功能开发,分支名
feature-*。每一个功能分支将会有一个功能分支的测试环境地址,如<branch>.dev.demo.com。 - 当功能分支测试完毕没有问题后,合并至主分支 master。将会随着主分支部署到生产环境。
- 当生产环境出现 Bug 时,切换一条新分支 hotfix-*,解决紧急 Bug。
为了保障代码质量,线上的代码必须通过 CI 检测,但是需要考虑以下
- 什么分支(监听范围)
- 什么事件(时间钩子)
- 什么命令(操作)
根据开发流程,可以得到以下结论,在功能分支以下事件
- 提交后(CI 阶段):进行 Build、Lint、Test、Preview 等,如未通过,则无法 Preview,更无法合并到生产环境分支进行上线
- 通过后(CI 阶段):合并到主分支,进行自动化部署。
企业里,主分支都是禁止直接推送,只能通过合并请求 PR 合并。所以只需要监听该事件,保障合并到主分支的代码纯净即可,也可以节省构建服务器的性能。
翻译成代码。
# 当功能分支代码提交 Pull Request 后,进行 CI
on:
pull_request:
types:
# 当新建了一个 PR 时
- opened
# 当提交 PR 的分支,未合并前并拥有新的 Commit 时
- synchronize
branches:
- 'main'
3. 任务的串行和并行
互不干扰的任务可以并行执行,虽然消耗构建服务器性能更多,但可以节省大量时间,很值当。
Lint 和 Test 互不干扰可以并行执行。但他们前置都需要 Install,这便是串行。 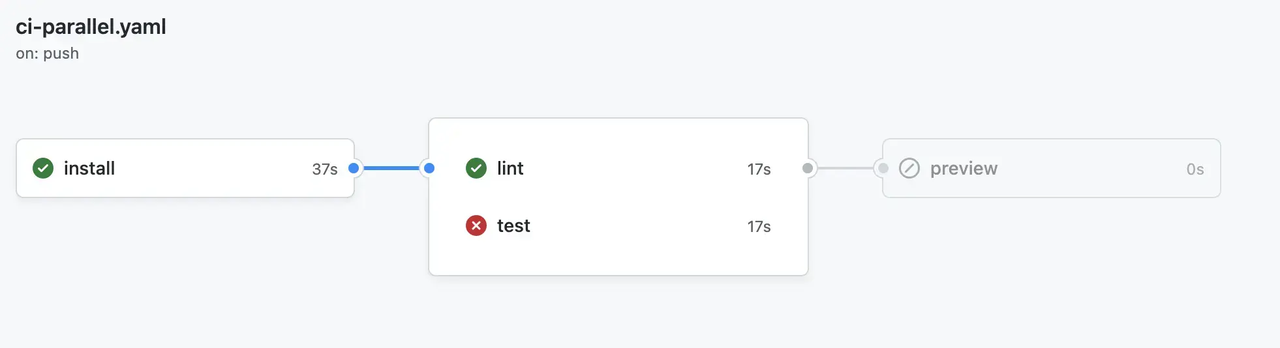
一般只要有任务失败,本次 CI 便意味着失败。但可以通过配置允许某些任务失败。jobs.<job_id>.continue-on-error
4 使用 Github Actions 进行 CI
由于 create-react-app 项目在打包过程中,会使用 ESLint Plugin 进行代码检查(源码),且根据 CI 环境决定报错还是警告。
所以此处可以使用 npm run build 模拟 Lint 检查。
编写 CI 配置 .github/workflows/ci.yaml
# 关于本次 workflow 的名字
name: CI
# 执行 CI 的时机: 当 git push 代码到 github 时
on: [push]
# 执行所有的 jobs
jobs:
lint:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
# 切出代码,使用该 Action 将可以拉取最新代码
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
# 配置 node.js 环境,此时使用的是 node14
# 注意此处 node.js 版本,与 Docker 中版本一致,与 package.json 中 engines.node 版本一致
# 如果需要测试不同 node.js 环境下的表现,可使用 matrix
- name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v1
with:
node-version: 14.x
# 安装依赖
- name: Install Dependencies
run: yarn
# 在 cra 中,使用 npm run build 来模拟 ESLint
- name: ESLint
run: npm run build
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v1
with:
node-version: 14.x
- name: Install Dependencies
run: yarn
- name: Test
run: npm run test
 二者已经是并行执行,还可以继续优化,将 Install 的过程抽离来减少服务器的并行压力。
二者已经是并行执行,还可以继续优化,将 Install 的过程抽离来减少服务器的并行压力。
5. 将 Install 过程前置
Install 前置会节省服务器资源,但并不会加快 CI 时间。甚至因为多了一个 Job,Job 间切换也需要花费时间,总时间还会略有增加。 
前置任务可以通过 needs 指定
install:
# codes
lint:
needs: install
test:
needs: install
完整配置文件
name: CI Parallel
on: [push] # 监听推送事件
jobs:
install: # 安装依赖
runs-on: ubuntu-latest # ubuntu 环境
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2 # 拉取代码
- name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v1 # 安装 node
with:
node-version: 14.x
- name: Cache Node Modules
id: cache-node-modules # 标志,用于 if
uses: actions/cache@v2 # 缓存,可以跟其他 Job 共享数据
with:
path: node_modules
key: node-modules-${{ hashFiles('yarn.lock') }} # 缓存标志,取 yarn.lock 文件 hash
restore-keys: node-modules-
- name: Install Dependencies
if: steps.cache-node-modules.outputs.cache-hit != 'true' # 无缓存,进行安装
run: yarn
lint:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
# 通过 needs 字段可设置前置依赖的 Job,比如 install
needs: install
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v1
with:
node-version: 14.x
- name: Cache Node Modules
id: cache-node-modules
uses: actions/cache@v2
with:
path: node_modules
key: node-modules-${{ hashFiles('yarn.lock') }}
restore-keys: node-modules-
- name: ESLint
run: npm run build
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
needs: install
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
- name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v1
with:
node-version: 14.x
- name: Cache Node Modules
id: cache-node-modules
uses: actions/cache@v2
with:
path: node_modules
key: node-modules-${{ hashFiles('yarn.lock') }}
restore-keys: node-modules-
- name: Test
run: npm run test
preview:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
needs: [lint, test]
steps:
- run: echo 'Preview OK'